TL;DR
Flask already serves static files by default, hence complying with the default structure allows the setup to be very easy.
Motivation
- Very fast setup of a local web server
- One deployment artefact can contain static and dynamic parts
Prerequisites
- Installed python
- Flask library is available
Approach
Default setup
Flask already serves static files by default. This Hello World example already serves static files on http://127.0.0.1:5000/static/.
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()Important are the parameters static_folder and static_url_path.
static_folder is the path to the folder containing the static files. The path can be relative to the application root_path or absolute. The constructor sets static_folder by default to ‘static’.
static_url_path is the path on which the static content is hosted defaulting to the value of static_folder.
These default values are set implicitly
app = Flask(__name__, static_folder='static', static_url_path=None)Host a simple website
To illustrate we create a folder called ‘static’ and add an example html file.
The directory structure should look like this: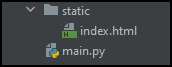
static/index.html file
<html>
<body>
<h1>Hello from the static folder!</h1>
</body>
</html>Running the application and opening http://127.0.0.1:5000/static/index.html we can see the example website.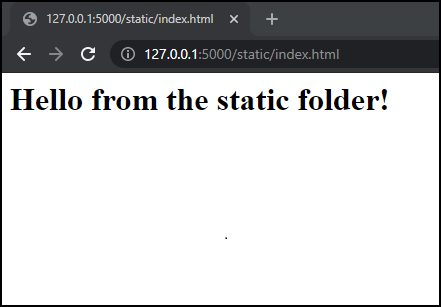
Change the root path
Personally, I prefer to host my website directly on the root path. To achieve this, static_url_path is set to ‘’.
Overwrite the default parameter
app = Flask(__name__, static_url_path='')Restart the application, and we can see the improved paths at http://127.0.0.1:5000/index.html.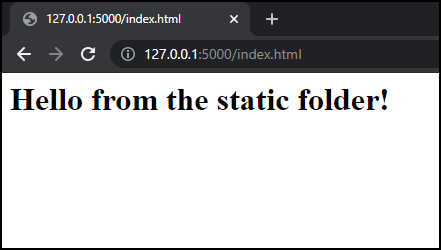
Further Reading
- Code can be found in this GitHub project.
- Often it is much easier to host the website in a storage bucket. GCP, AWS and Azure provide guidelines for this.
- Also containerized solutions with NGINX or Apache HTTP Server are much more common.
- One advantage of this approach is the creation of one deployment artefact that can include frontend and backend.
- The costs can be quite high for a website with high traffic. Please check your cloud billing estimations beforehand.
- To reduce costs you can use CDNs and other caching mechanisms.